The primary objective is to get a good first draft of the process flow diagram.
To get insight into the current process, brown paper process mapping is a tool that is commonly used. State of the art
BPM tools make it possible to do map the process directly in the tool.
-
When using workshops, the preparation is essential: arrange rooms, materials and most important of all the right
participants. E.g. involve the process owner, executioners, suppliers, customer representatives.
-
Starting from events/triggers – “you sit behind your desk, when do you start to act” – determine the process steps
that are taken. As said before, brown paper process mapping is a convenient tool, but it is also possible to do
this online.
-
Beware of the scope. Don’t try to get all information in one workshop, focus on the operational process aspects:
-
What events/triggers can you distinguish.
-
What is the sequence of process steps (and try to record some description per step) started by every
event/trigger?
-
What roles are involved? A very useful technique here can be RACI schemes.
-
What automated support is used in order to be able to execute this process?
-
Information usage
-
Operational reporting
Organize a workshop to finalize the business processes.
Preparation
-
Participants: process owner, stakeholder, executioners, internal supplier/customer, IT support
Input
-
Product, market, channel, customer analysis
-
High level process flow diagram
-
Value added chains level 1, 2, 3
-
Process allocation matrix
-
Prepared draft process flow diagrams
Execution
-
Present the high level process flow diagram // L3 value added chain.
-
Present the L4 process flow diagram and validate it. Especially focus on the interfaces to other processes where a
customer-supplier relationship exists. Within the process flows ensure (if applicable) to describe:
-
Process steps
-
Process triggers / events
-
Suppliers
-
Customers
-
People involved (RASCI-VS) - differentiate in roles, actors and people/organization
-
Business services / application usage
-
Business & information objects
-
Document usage
-
Process interfaces and handovers
-
Process performance indicator
-
Milestones
-
Risks & measures of control (refer to GRC current state)
The information (‘attributes’) that you want to model at both process and activity level depend on the engagement’s
objective. One can imagine that for a efficiency improvement engagement completely different attributes are important
compared with a internal controls engagement. In the first case you will be interested in cycle times, waiting times,
volume fluctuations, buffers, quantities, etc., whereas in the second case you want to exactly know who is doing what,
what controls are built in, etc.
-
Document process pain points
-
Document process opportunities
-
Document process Strengths
Output
-
Process flow diagrams, including RASCI-VS and KPI’s
-
Process Strengths
-
Process Pain points
-
Process Opportunities
Sign off business process by process owner.
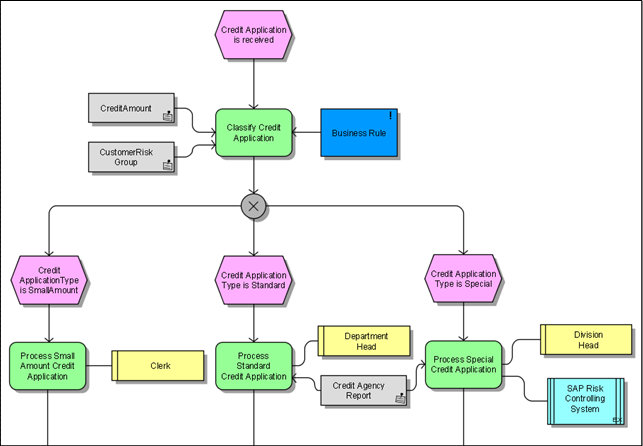
Example of process flow (modelled in ARIS):
|